In the world of modern manufacturing, precision is everything. As industries strive for improved accuracy, speed, and repeatability in their production processes, CNC machining has become a crucial technology. At the core of CNC machining lies an often-overlooked component: CNC fixtures. These tools play a pivotal role in securing the workpiece in place, ensuring that it is accurately machined according to specifications. This article explores the function, importance, and various types of CNC fixture that enhance the overall machining process.
1. What Are CNC Fixtures?
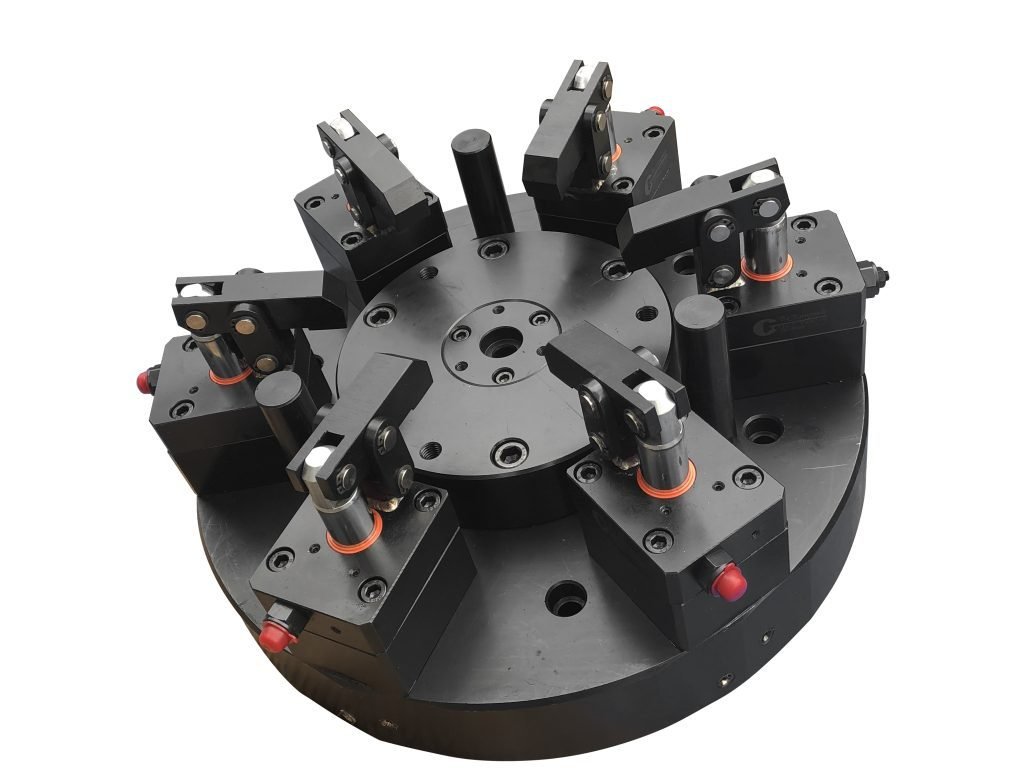
A CNC fixture is a mechanical tool used to hold and position a workpiece on a CNC machine during the machining process. Its primary function is to secure the part firmly in place so that cutting, drilling, milling, or other machining operations can be carried out with precision and repeatability. The fixture ensures that the workpiece remains stationary while the CNC machine performs complex tasks, reducing errors caused by movement, misalignment, or vibration.
Fixtures are specifically designed for each workpiece and machining operation. They are built to adapt to different shapes, sizes, and materials of parts, and can vary in complexity, from simple vices and clamps to highly specialized custom fixtures.
2. Why CNC Fixtures Are Essential
The use of CNC fixtures is essential for several reasons. These reasons are not just related to the efficiency of the machining process, but also the quality and precision of the final product.
2.1. Improved Precision
The primary reason for using a CNC fixture is to ensure precise alignment of the workpiece. Fixtures ensure that the part is held securely in the desired position, preventing it from shifting during the machining process. This is especially important for producing parts that need to meet strict tolerances, such as those used in aerospace, automotive, or medical applications.
2.2. Increased Efficiency
CNC fixtures increase the overall efficiency of machining by reducing the time spent on workpiece setup and repositioning. Once the fixture is set up, it can hold multiple parts in place for high-volume production. This leads to faster cycle times and higher throughput, as CNC machines can work uninterrupted, with minimal downtime for setup changes.
2.3. Consistency and Repeatability
For mass production runs, consistency is key. CNC fixtures enable the production of identical parts without variation, ensuring high repeatability. This consistency is essential for industries that require large quantities of the same part, such as electronics, automotive, and industrial equipment manufacturing.
2.4. Reduces Human Error
Manual clamping and positioning can introduce significant variability and human error in the machining process. CNC fixtures minimize the need for operator involvement by automating the part-holding process. This reduces the risk of incorrect clamping and alignment, leading to better outcomes with fewer mistakes.
2.5. Minimizes Workpiece Damage
CNC fixtures are designed to securely hold the workpiece without causing damage. Unlike traditional clamps, which can leave marks or indentations, fixtures are built to apply the right amount of force in the right places. This ensures that the workpiece is firmly in place but not harmed during the process.
3. Types of CNC Fixtures
There are various types of CNC fixtures, each suited for specific tasks and workpieces. Choosing the right fixture depends on factors such as the workpiece material, geometry, and machining operation. Here are the most common types of CNC fixtures:
3.1. Vices
CNC vices are among the most commonly used fixtures in CNC machining. These vices clamp the workpiece between two jaws, holding it firmly in place during milling or drilling. CNC vices are widely used for simple, flat parts, but their versatility also allows them to accommodate a range of materials and sizes.
- Applications: Milling, drilling, surface grinding.
- Advantages: Easy to use, versatile, can handle a variety of workpieces.
3.2. Clamps
CNC clamps are tools used to secure workpieces with irregular shapes or those that are difficult to clamp with a vice. There are different types of clamps, such as toggle clamps, screw clamps, and vacuum clamps, each designed for specific applications. CNC clamps are ideal for holding parts with non-flat surfaces or high-volume workpieces that need to be changed quickly.
- Applications: CNC turning, milling, and drilling.
- Advantages: Flexible, ideal for irregularly shaped parts.
3.3. Custom Fixtures
Custom CNC fixtures are designed specifically for a unique workpiece. These fixtures are often used when off-the-shelf vices or clamps cannot provide the necessary support or precision for a particular part. Custom fixtures can accommodate complex geometries, intricate features, or tight tolerances that require a high degree of precision.
- Applications: Aerospace components, custom parts, and specialized projects.
- Advantages: Tailored to specific workpieces, ensures high accuracy.
3.4. Pallet Fixtures
Pallet fixtures are used in systems where multiple parts are loaded onto a pallet. These fixtures are part of a palletized CNC system, where several parts can be machined simultaneously. The pallet allows for quick changeovers between different workpieces, and the fixture holds each part securely during machining operations. Pallet systems are especially useful in automated or high-volume production.
- Applications: Mass production, automation, high-volume operations.
- Advantages: High throughput, reduced downtime.
3.5. Collet Fixtures
Collet fixtures use a collet—a type of clamp that grips cylindrical workpieces—by applying radial force. Collet fixtures are ideal for machining parts with round or cylindrical geometries, such as shafts or tubes. Collets provide a secure grip without damaging delicate or precision parts.
- Applications: CNC turning, rotary machining.
- Advantages: Precise clamping, ideal for cylindrical parts.
3.6. Magnetic Fixtures
Magnetic fixtures rely on magnetic force to hold ferrous workpieces in place. These fixtures are highly convenient for tasks that require quick setup or frequent changes in the workpiece. Magnetic fixtures are especially useful in milling operations where access to flat surfaces is necessary. They offer the advantage of holding parts without mechanical clamping, allowing for fast and efficient workpiece changes.
- Applications: Milling, surface grinding, drilling.
- Advantages: Quick setup, no mechanical clamping required.
4. Materials Used for CNC Fixtures
The materials used for CNC fixtures must be carefully selected based on factors like rigidity, durability, and cost. The material should also be compatible with the type of machining operation being performed. Some common materials used in CNC fixture construction include:
4.1. Steel
Steel is the most common material for CNC fixtures due to its durability and strength. Steel fixtures are capable of withstanding the high forces involved in machining and are ideal for heavy-duty operations. Steel also has the advantage of being easy to machine and repair.
4.2. Aluminum
Aluminum is a lightweight alternative to steel and is often used for fixtures that require less weight or for parts that need to be machined quickly. Aluminum fixtures are typically used in industries such as aerospace, where weight is a critical factor.
4.3. Cast Iron
Cast iron is known for its stability and ability to absorb vibrations, making it a good choice for CNC fixtures used in precision machining operations. Cast iron fixtures can provide high rigidity, making them suitable for high-precision tasks.
4.4. Polymer Composites
Polymer composites are used for specific applications where high strength-to-weight ratios are needed. These materials are lighter than steel and aluminum, making them useful in high-speed or high-precision operations.
5. Factors to Consider When Designing CNC Fixtures
Designing an effective CNC fixture involves several considerations to ensure it performs optimally during machining. Key factors include:
5.1. Workpiece Geometry
The fixture design must accommodate the shape, size, and features of the workpiece. Irregularly shaped parts may require custom features like supports, pins, or brackets to ensure they are held securely during machining.
5.2. Material Compatibility
The fixture material must be suitable for the type of workpiece being machined. For example, fixtures used for cutting hard materials like titanium or steel must be made of highly durable materials like hardened steel or cast iron.
5.3. Tool Access
The fixture design must allow sufficient access for the CNC tool to reach all areas of the workpiece that need to be machined. This includes ensuring that the fixture does not obstruct the cutting tool’s path.
5.4. Easy Setup and Removal
CNC fixtures should be easy to set up and remove to minimize downtime between operations. Features like quick-change systems or adjustable clamps can make fixture setup more efficient.
6. Conclusion
CNC fixtures are indispensable tools in CNC machining that ensure workpieces are held securely, accurately, and consistently during the manufacturing process. The right fixture can improve precision, efficiency, and repeatability, making it easier to produce high-quality parts for a wide range of industries. With various types of fixtures available, including vices, clamps, custom fixtures, and magnetic systems, manufacturers can select the ideal fixture for each specific application. Ultimately, CNC fixtures help drive efficiency and reduce costs, contributing to the success of modern manufacturing operations.