Why Solar Energy is More Important Than Ever
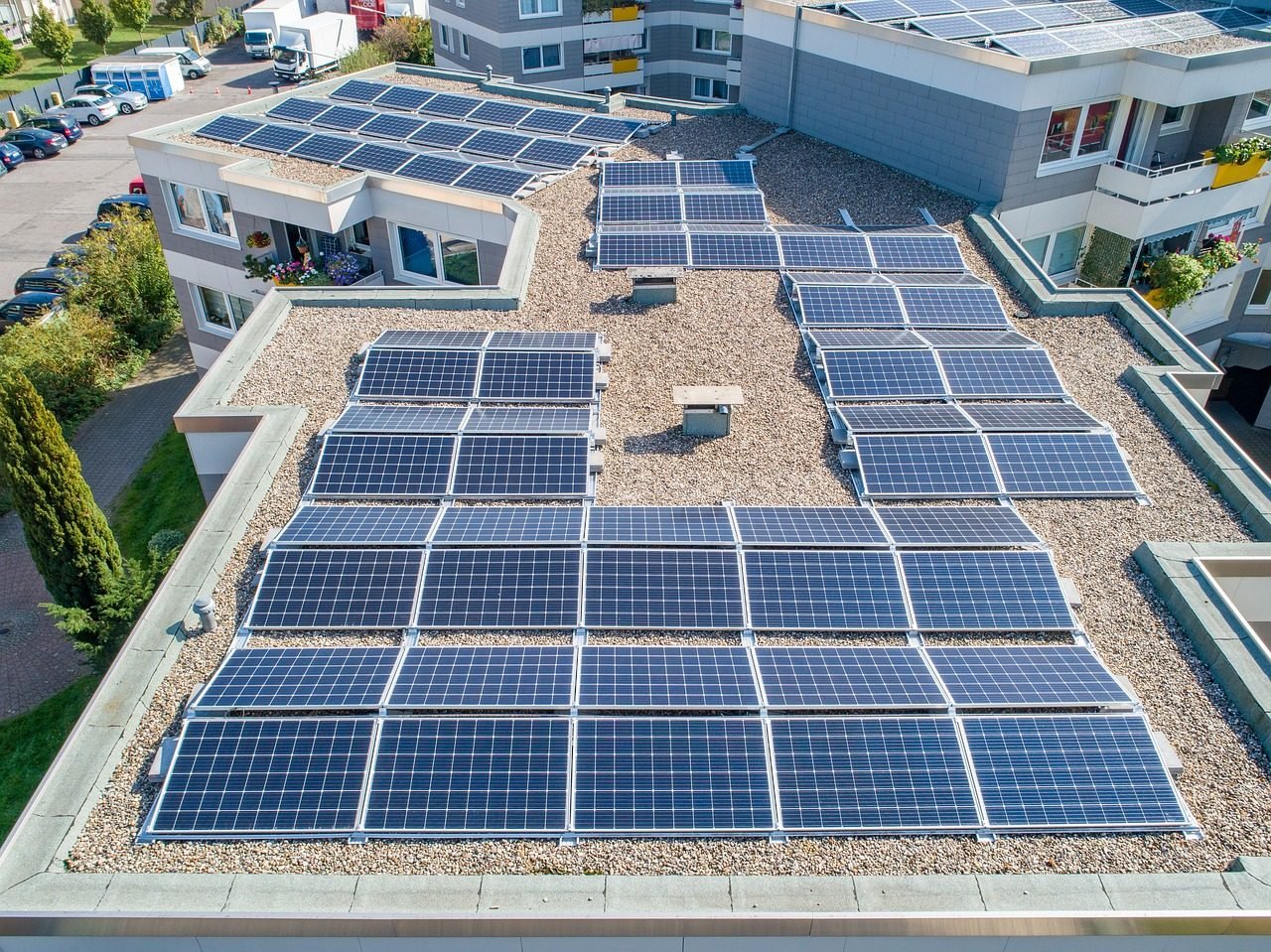
As the world grapples with climate change, the demand for clean, renewable energy sources has surged. Solar power, with its capacity to generate electricity without carbon emissions, is at the forefront of this transformation. Unlike fossil fuels, solar energy harnesses the sun’s rays—a virtually inexhaustible resource—and can be deployed in a variety of environments.
Moreover, solar energy has become more affordable as production costs continue to fall. According to recent data, the cost of solar power has decreased by over 80% in the past decade, making it one of the cheapest forms of energy available. This affordability, combined with increased efficiency, positions solar as a critical component of the global transition to a low-carbon future.
Key Trends Shaping the Future of Solar Energy
Increased Solar Efficiency with Perovskite Cells
One of the most promising advancements in solar technology is the development of perovskite solar cells. Unlike traditional silicon-based cells, perovskite cells are made from a new class of materials that offer high efficiency and lower production costs. Researchers have already achieved impressive efficiencies with perovskite cells, and they have the potential to be even more cost-effective than silicon.
These cells are also more versatile, as they can be manufactured in flexible and lightweight forms, making them suitable for applications beyond traditional solar panels, such as windows, roofs, and even clothing. Although perovskite cells are still in the experimental stage, their commercialization could revolutionize the solar industry in the coming years.
Floating Solar Farms
With limited land availability, especially in densely populated urban areas, floating solar farms have emerged as a valuable solution. These installations, which involve placing solar panels on bodies of water, offer several benefits. For one, they reduce the need for land, allowing more space to be used for agricultural or urban development.
Floating solar also has efficiency advantages, as the water helps keep the panels cool, which improves their performance. Countries like China and Japan are leading the way in adopting floating solar technology, and it’s expected that this trend will grow as more regions face space and resource constraints.
Solar Energy Storage Solutions
One of the biggest challenges with solar energy is its intermittent nature—solar power is only generated when the sun is shining. However, advancements in energy storage technology are paving the way for round-the-clock solar power. Batteries, especially lithium-ion and new solid-state options, are becoming more efficient and affordable, allowing excess solar energy to be stored and used when needed.
Tesla’s Powerwall and other home energy storage systems are good examples of how storage can support residential solar setups. At a larger scale, solar-plus-storage solutions are being deployed in utility-scale solar farms, enabling grid stability and energy availability even during cloudy days or at night.
Technological Innovations Revolutionizing Solar Panels
Bifacial Solar Panels
Bifacial solar panels are a recent innovation that captures sunlight on both sides of the panel, increasing overall energy output. The back of the panel can capture reflected sunlight from the ground, which is especially effective in snowy or reflective environments. These panels have already shown efficiency gains of up to 30% compared to traditional monofacial panels, making them an attractive option for large solar installations.
Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV)
Building-integrated photovoltaics represent another exciting innovation, integrating solar cells into building materials like windows, roofs, and facades. Tesla’s Solar Roof is a well-known example, where photovoltaic cells are embedded directly into roof tiles. This technology not only saves space but also creates aesthetically pleasing designs for buildings, making it an attractive option for urban areas.
BIPV technology is especially valuable in cities where space is limited, and energy demands are high. As more building codes require renewable energy sources, BIPV could become a standard feature in future urban development.
Thin-Film Solar Cells
Thin-film solar cells are made by depositing photovoltaic materials onto a substrate, making them lightweight, flexible, and highly adaptable. These cells are less efficient than traditional panels but can be applied in various unconventional settings, like portable solar chargers, vehicle rooftops, and even clothing. Thin-film technology is expected to see further development, expanding its applications and driving costs down.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence and IoT in Solar Technology
Artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) are transforming how we monitor, manage, and optimize solar power systems. Smart energy management platforms use AI algorithms to predict energy production, monitor system health, and optimize performance in real-time. IoT sensors and devices can track metrics like temperature, energy output, and shading, allowing for immediate adjustments and efficiency improvements.
By integrating AI and IoT, solar installations can operate more efficiently, reducing maintenance costs and maximizing output. This combination also enables better grid management, as energy providers can respond dynamically to changes in supply and demand.
Challenges and Opportunities in the Solar Sector
While solar energy is booming, challenges remain, especially in the areas of land use, resource availability, and efficiency. The production of solar panels requires rare materials like silicon, silver, and indium, which are finite resources. Recycling solar panels is also a growing concern, as the current infrastructure for panel disposal is insufficient to handle the expected volume of retired panels.
However, these challenges create opportunities for innovation. New research is underway to develop panels that use fewer rare materials, and governments are creating incentives for recycling programs. Furthermore, innovations like solar panel leasing, community solar programs, and pay-as-you-go solar financing are making solar power accessible to a broader population.
The Future of Solar Energy in Urban and Rural Areas
Solar power is adaptable and versatile, making it suitable for both urban and rural settings. In cities, where space is limited, innovations like vertical solar farms and building-integrated photovoltaics are transforming buildings into power generators. In rural and remote areas, solar energy is providing a reliable source of electricity where traditional power infrastructure is costly or unavailable.
Community solar programs are also gaining popularity, allowing multiple households to share the benefits of a single solar installation. This model is particularly effective in lower-income communities, as it reduces the upfront costs associated with individual solar systems.
The Road Ahead: Solar’s Role in the Global Energy Mix
As solar technology continues to evolve, it is expected to play a significant role in the global energy mix. According to the International Energy Agency, solar energy could account for nearly a third of the world’s electricity by 2050 if current growth trends continue. With falling costs, improved efficiency, and increased accessibility, solar power has the potential to become the leading source of renewable energy worldwide.
Governments, businesses, and individuals all have roles to play in supporting solar growth. Policies that promote renewable energy adoption, investments in research and development, and incentives for installing solar power systems are crucial to the sector’s success.
Conclusion
The future of solar energy is bright and full of possibilities. As technological advancements continue to break new ground, solar power is becoming more accessible, efficient, and versatile. From perovskite cells to building-integrated photovoltaics, the innovations in solar technology are not only making solar power more effective but also more integrated into our daily lives. With sustained investment and policy support, solar energy can be a cornerstone of a cleaner, more sustainable energy future.
FAQs
1. What is the most significant trend in solar technology right now?
The development of perovskite solar cells is one of the most exciting trends, as these cells could significantly increase efficiency and reduce costs.
2. How does solar energy storage work?
Solar energy storage systems, like lithium-ion batteries, store excess energy generated during sunny periods for use at night or during cloudy days.
3. What are bifacial solar panels?
Bifacial solar panels capture sunlight on both sides, increasing energy output by capturing reflected sunlight from the ground.
4. Can solar power be used in cities with limited space?
Yes, innovations like building-integrated photovoltaics and vertical solar farms are making solar power accessible in space-limited urban areas.
5. How does AI contribute to solar energy?
AI helps optimize solar systems by predicting energy production, tracking system performance, and making real-time adjustments for maximum efficiency.