Menu

A digital marketing agency specializing in SEO and paid ads helps businesses achieve strong online visibility and consistent growth. By combining long-term organic search strategies with performance-based advertising, agencies attract targeted traffic and improve conversion rates. SEO builds authority and sustainable rankings, while paid ads deliver immediate reach and measurable results. A data-driven approach, continuous optimization, and transparent reporting ensure campaigns remain effective over time. Choosing the right digital marketing partner allows businesses to maximize return on investment, strengthen brand presence, and stay competitive in the evolving digital landscape.

A digital marketing agency specializing in SEO and paid ads helps businesses achieve strong online visibility and consistent growth. By combining long-term organic search strategies with performance-based advertising, agencies attract targeted traffic and improve conversion rates. SEO builds authority and sustainable rankings, while paid ads deliver immediate reach and measurable results. A data-driven approach, continuous optimization, and transparent reporting ensure campaigns remain effective over time. Choosing the right digital marketing partner allows businesses to maximize return on investment, strengthen brand presence, and stay competitive in the evolving digital landscape.

In an increasingly globalized world, individuals and businesses often face the challenge of having their official documents recognized and accepted in foreign countries. When it comes to dealing with Germany,
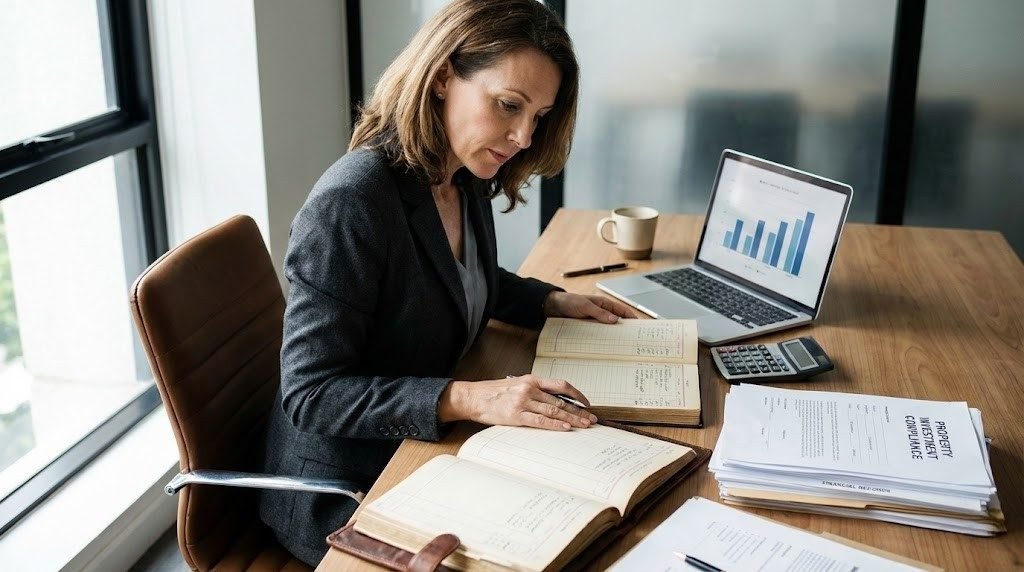

A property investment company in Singapore offers clarity, control, and flexibility when managed correctly. Tax and compliance require ongoing attention throughout the investment lifecycle. Focus on fundamentals.
Computer vision has become a core component of modern artificial intelligence systems, powering applications such as autonomous vehicles, facial recognition, healthcare diagnostics, smart surveillance, and retail analytics. At the heart

Experience the goodness of pure A2 cow ghee. Healthy, easy to digest, and perfect for cooking and wellness. Discover its benefits today.
We hope this read was helpful to you! Don’t forget to follow Guest Genius Hub for more relevant and informative content!