Introduction
The drive shaft is an essential component in many vehicles and machinery, playing a crucial role in transferring power from the engine or motor to the wheels or other driven components. Despite being a relatively simple mechanical part, its design, maintenance, and performance have a significant impact on a vehicle’s efficiency and reliability. This article explores the function, types, components, and importance of drive shafts in modern automotive and industrial applications.
Definition
A drive shaft is a mechanical component used in vehicles and machinery to transmit torque and rotational power from the engine or motor to the wheels, axles, or other driven components. It is typically a tubular steel or aluminum shaft with universal joints at both ends, allowing it to accommodate movement and misalignment while efficiently delivering power. Drive shafts are essential in rear-wheel-drive, all-wheel-drive, and some front-wheel-drive vehicles, as well as in various industrial applications.
What is a Drive Shaft?
A drive shaft, also known as a propeller shaft or cardan shaft, is a mechanical component used to transmit torque and rotation. In vehicles, it typically connects the transmission to the differential, ensuring that power is delivered to the wheels efficiently. Drive shafts are commonly found in rear-wheel drive, all-wheel drive, and four-wheel drive vehicles, as well as in various industrial applications like heavy machinery and marine propulsion systems.
How Drive Shafts Work
The primary function of a drive shaft is to transfer rotational force from the engine to the wheels or other moving parts of a machine. When the engine generates power, the transmission adjusts the torque and sends it to the drive shaft. The shaft then transmits this torque to the differential, which distributes it to the wheels, allowing the vehicle to move.
Since vehicles and machinery experience variations in movement and alignment, drive shafts must be flexible enough to accommodate these changes while maintaining efficient power transmission. Universal joints (U-joints) and constant velocity (CV) joints help the shaft adapt to these variations without losing efficiency or causing mechanical failure.
Components of a Drive Shaft
A drive shaft is composed of several key components that work together to ensure smooth power transmission:
- Shaft Tubing – The main body of the drive shaft, usually made from steel, aluminum, or carbon fiber, designed to withstand high torque and rotational speeds.
- Universal Joints (U-Joints) – These flexible joints allow the drive shaft to accommodate changes in angles and movement, preventing excessive strain on the transmission and differential.
- Slip Yoke – A component that connects the drive shaft to the transmission, allowing for slight variations in length due to suspension movement.
- Center Bearing (if applicable) – Found in longer drive shafts, it supports the shaft and minimizes vibrations.
- CV Joints – These joints provide smoother power transmission by maintaining constant velocity at different angles, commonly used in front-wheel drive and all-wheel drive vehicles.
- Flanges and Couplings – These are connection points that help secure the drive shaft to the transmission, differential, or other components.
Types of Drive Shafts
Drive shafts come in various designs depending on the vehicle or machinery they are used in. Some common types include:
- Single-Piece Drive Shaft – Used in short-wheelbase vehicles, offering simplicity and strength.
- Two-Piece Drive Shaft – Common in longer vehicles, incorporating a center bearing to provide additional support and reduce vibrations.
- CV Drive Shaft – Uses constant velocity joints to deliver power smoothly, typically found in front-wheel drive and all-wheel drive vehicles.
- Slip Joint Drive Shaft – Features a slip yoke to allow changes in length, useful in vehicles with significant suspension travel like off-road vehicles.
Importance of Drive Shafts
Drive shafts are crucial for ensuring smooth and efficient power transmission. Here are some reasons why they are essential:
Efficient Power Delivery – Without a properly functioning drive shaft, the power from the engine would not reach the wheels effectively, leading to poor vehicle performance.
Smooth Operation – Drive shafts, especially those with CV joints, reduce vibrations and jerky movements, enhancing driving comfort.
Durability and Strength – A well-designed drive shaft can handle high torque and rotational speeds without failure, making it essential for heavy-duty applications.
Flexibility and Adaptability – With the help of U-joints and CV joints, drive shafts accommodate different angles and movement variations, ensuring consistent performance.
Critical for All-Wheel Drive and 4WD Vehicles – In all-wheel and four-wheel drive systems, drive shafts enable power distribution to multiple wheels, improving traction and off-road capability.
Common Drive Shaft Problems and Maintenance Tips
Like any mechanical component, drive shafts can experience wear and tear over time. Some common issues include:
- Vibrations – Often caused by imbalanced drive shafts, worn-out U-joints, or misalignment.
- Clunking Noises – Can result from loose or worn-out U-joints.
- Difficulty in Turning – May be due to faulty CV joints restricting movement.
- Excessive Play – A damaged slip yoke or worn-out bearings can lead to excessive movement in the drive shaft.
Maintenance Tips
- Regular Inspection – Periodically check the drive shaft for signs of damage, rust, or excessive wear.
- Lubrication – Keep U-joints and CV joints properly lubricated to prevent friction and wear.
- Balancing – Ensure the drive shaft is balanced correctly to avoid vibrations.
- Timely Replacement – If any component is excessively worn or damaged, replace it promptly to prevent further issues.
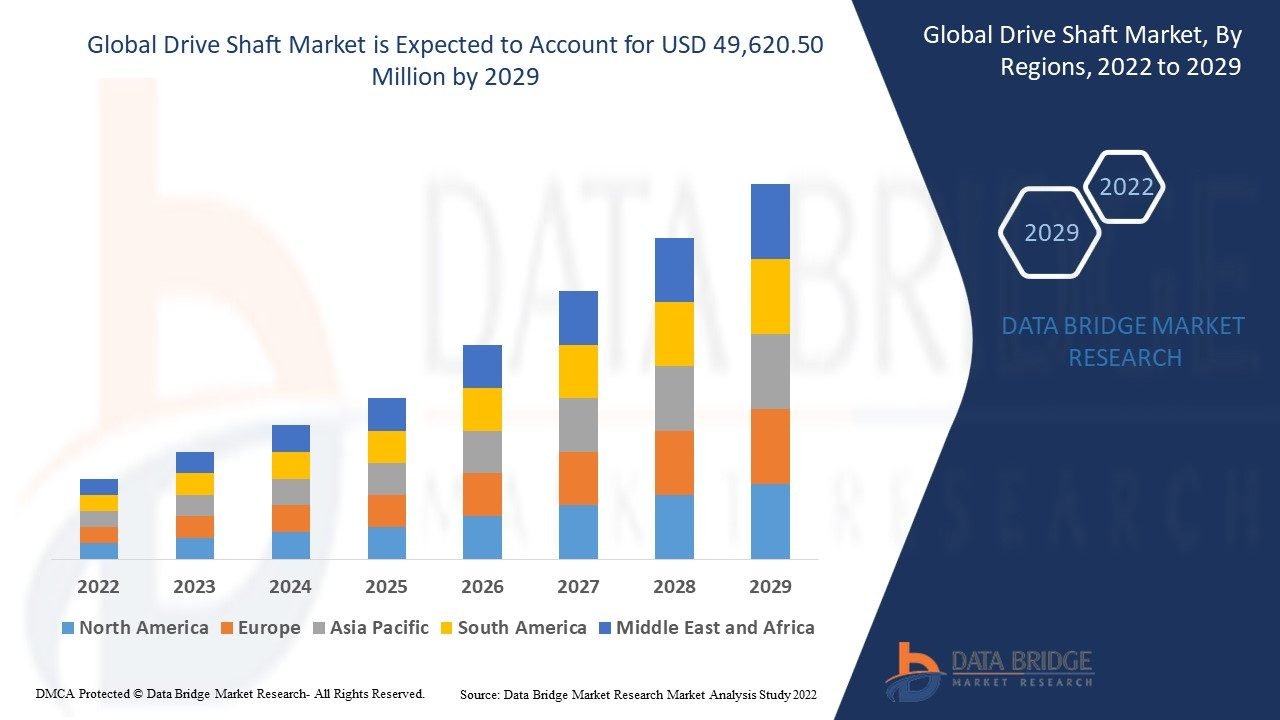
Growth Rate of Drive Shaft Market
According to Data Bridge Market Research, the drive shaft market was estimated to be worth USD 17.72 billion in 2024 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.61% from 2025 to 2032, reaching USD 27.42 billion.
Read More: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-drive-shaft-market
Future Trends of Drive Shaft Market
Growing Demand for Lightweight Materials:
Weight reduction is a significant factor in the automotive industry, as it directly impacts fuel efficiency and vehicle performance. The adoption of lightweight materials such as carbon fiber and aluminum in drive shaft manufacturing is gaining traction. These materials offer enhanced strength while reducing overall vehicle weight, leading to improved fuel economy and lower emissions.
Rising Adoption of Electric Vehicles (EVs):
The increasing shift toward electric mobility is influencing the drive shaft market. Unlike conventional internal combustion engine vehicles, EVs require specialized drive shafts designed to handle instant torque and high-speed operation. As the EV market expands, manufacturers are focusing on developing drive shafts with optimized performance and durability.
Integration of Advanced Manufacturing Technologies:
The use of advanced manufacturing technologies such as 3D printing and precision machining is enhancing drive shaft production. These technologies allow for the creation of complex geometries, improved material properties, and cost-effective production. As automation and AI-driven design tools become more prevalent, the efficiency and quality of drive shafts will continue to improve.
Increased Demand for All-Wheel Drive (AWD) and Four-Wheel Drive (4WD) Vehicles:
The popularity of AWD and 4WD vehicles, especially in SUVs and off-road vehicles, is driving the demand for robust and efficient drive shafts. Consumers are increasingly opting for vehicles with better traction and stability, leading to a higher need for advanced drive shaft systems that can withstand extreme conditions.
Emphasis on Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Production:
Environmental regulations and sustainability goals are pushing manufacturers to adopt eco-friendly production processes. The use of recyclable materials, energy-efficient manufacturing techniques, and sustainable supply chain management are becoming key focus areas in the drive shaft industry.
Growing Market in Emerging Economies:
Emerging economies, particularly in Asia-Pacific and Latin America, are witnessing significant growth in automotive production and sales. The expanding middle-class population, urbanization, and infrastructure development are contributing to increased demand for vehicles, thereby boosting the drive shaft market.
Conclusion
Drive shafts are an integral part of automotive and industrial machinery, ensuring efficient power transmission and smooth operation. Understanding their function, types, and maintenance requirements can help vehicle owners and operators maintain performance and longevity. Regular inspections and proper care can prevent costly repairs and keep vehicles running efficiently. Whether in a passenger car, a truck, or industrial machinery, the drive shaft plays a pivotal role in motion and power delivery.