Investing is one of the most effective ways to build wealth over time. However, understanding the nuances of how different financial factors affect your investments is crucial. One such factor is the Cost Inflation Index (CII), a critical component for calculating long-term capital gains in India. This article explores what the Cost Inflation Index is, its significance, especially for the year 2024-25, and its impact on investments.
Understanding the Cost Inflation Index
The Cost Inflation Index for 2024-25 is a measure used in India to calculate the inflation-adjusted increase in the value of assets. Simply put, it helps an investor understand how much the purchasing power has degraded over time due to inflation. The CII is determined by the government and is primarily used to compute the inflation-adjusted cost of an asset, thus aiding in the calculation of long-term capital gains tax.
How is the Cost Inflation Index Determined?
The Cost Inflation Index for a specific financial year is notified by the Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT). It reflects the level of inflation based on the Consumer Price Index. The base year for the Cost Inflation Index is 2001-02, and the CII for this base year is set at 100. To determine the adjusted or indexed cost of acquisition, the CII for the year 2024-25, for example, would be compared to the CII of the base year.
Calculating Long Term Capital Gains
In India, long term capital gains tax is applicable to profits realized from the sale of assets held for more than 24 months for real estate, and 12 months for other assets like equities. The formula to calculate the long-term capital gains is as follows:
Long-term capital gains (LTCG) = Sale value – Indexed cost of acquisition and improvement
To calculate the indexed cost of acquisition, the formula is:
Indexed cost of acquisition = (Cost of acquisition CII of sale year) / CII of purchase year
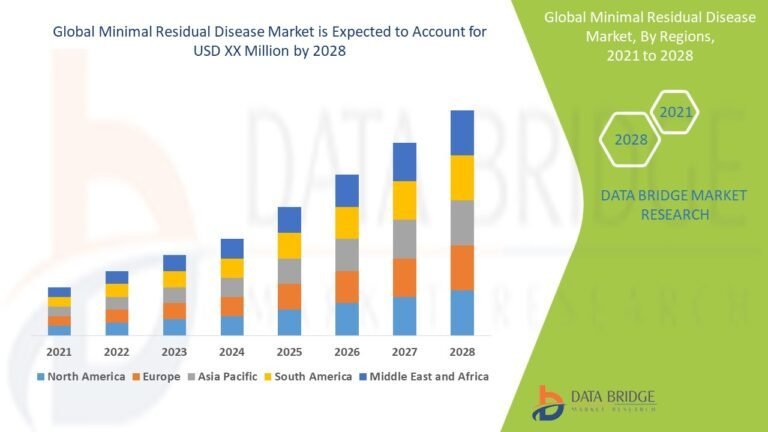
Impact for the Financial Year 2024-25
To comprehend the CII’s impact for investors during the financial year 2024-25, consider an example where an investor bought a property in March 2010 for INR 10,00,000 and sold it in April 2024 for INR 50,00,000. Assume the CII for 2009-10 was 148, and for 2024-25, say it’s announced as 350 (hypothetical value for illustration).
[text{Indexed cost of acquisition} = left(frac{10,00,000 times 350}{148}right) approx INR 23,64,865]
Therefore, the long-term capital gain would be:
[text{LTCG} = 50,00,000 – 23,64,865 = INR 26,35,135]
In this scenario, the indexed cost helps the investor reduce the taxable gain due to inflation, thus lowering the capital gains tax burden.
Importance of Cost Inflation Index for 2024-25
The Cost Inflation Index for 2024-25 plays a vital role for investors who plan on realizing their investments in that financial year. It allows them to account for inflation, ensuring that the tax they pay is only on real gains. By neutralizing the inflation component, the Cost Inflation Index helps prevent erosion of profits due to the mere effect of price rise over the years.
Impact on Investment Decisions
Given its influence on taxable profits, the Cost Inflation Index significantly impacts investment decisions. Knowledge of CII helps investors plan the timing of their asset sales and purchase more effectively. Long-term investors regularly consider CII when planning portfolio redistribution or assets liquidation, to ensure they maximize the post-tax returns on their investments.
Investors must also be mindful of the government policies interfering with the calculation of CII, as changes in financial guidelines can influence how gains are computed. Understanding this metric’s foundation helps investors make more informed decisions about when to buy or sell assets.
Conclusion
In summary, the Cost Inflation Index is an indispensable tool for investors, particularly for those engaged in long-term asset accumulation. It not only provides a mechanism for adjusting the cost of acquisition with regards to inflation but also plays a critical role in the assessment of long-term capital gains liabilities. Informed decision-making based on an understanding of CII can lead to more tax-efficient investment strategies.
Summary
The Cost Inflation Index (CII) stands as a significant element in the computation of long-term capital gains for investors in India. As outlined, the CII adjusts the cost of asset acquisition to account for inflation, ensuring that taxes are levied on real, rather than inflationary, gains. For the fiscal year 2024-25, the CII is poised to impact investment strategies as it determines the extent of tax liability on realized gains. By factoring in the CII, long-term investors can potentially reduce their taxable income, thereby optimizing their investment returns. However, it remains imperative for investors to comprehensively evaluate the multiple facets of investing in the Indian financial landscape, using CII as one of many analytical tools to formulate their strategies.
Disclaimer: This content is for informational purposes only and should not be construed as financial or investment advice. Investors are urged to thoroughly evaluate the risks and benefits of trading or investing in the Indian financial markets and consult with a qualified financial advisor to tailor strategies according to their individual circumstances.